For anyone who travels, goes camping, or lives off the grid, selecting the appropriate cooler is crucial. Compressor coolers and absorption coolers, two kinds of refrigeration systems intended to keep food and drinks cold without only using ice, are among the most widely used choices. Although both provide powered cooling, it’s crucial to know which choice best suits your needs because they differ greatly in terms of technology, efficiency, and optimal use cases.
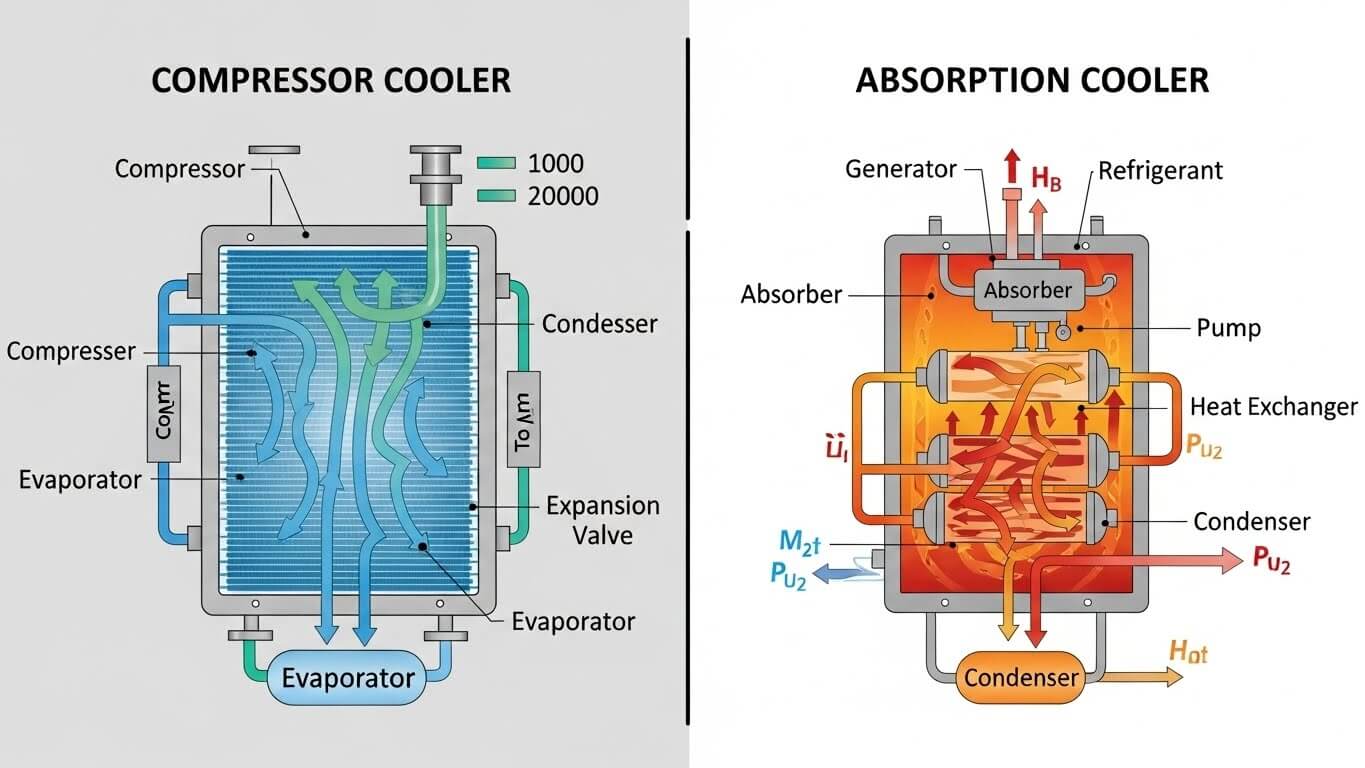
A compressor cooler functions similarly to a conventional refrigerator. It provides accurate temperature control and quick cooling by actively cooling the interior with a compressor and refrigerant. These coolers are quite efficient; they can swiftly drop temperatures and continue to operate consistently even in hot weather. Compressor coolers are well-liked by RV owners, tourists, and everyone else who requires reliable freezing or cooling capabilities due to their speed and dependability.
An absorption cooler, on the other hand, uses a different mechanism that drives a chemical absorption cycle utilizing a heat source, such as gas, AC power, or 12V DC. This system is perfect for use in RVs, boats, and other environments where noise and mechanical movement are issues because it is silent and vibration-free. Although absorption coolers are quite adaptable when it comes to power sources, they typically cool more slowly and may find it difficult to maintain very low temperatures in hot conditions.
Depending on how you intend to use it, where you’ll be traveling, and how rapidly you need stuff chilled, you can choose between an absorption cooler and a compressor. The ideal option depends on a number of factors, including cooling performance, power availability, portability, noise, and long-term value.
The main distinctions between compressor and absorption coolers—performance, energy efficiency, mobility, cost, and optimum user scenarios—will be examined in this comparison. By the time it’s all over, you’ll know exactly what kind of cooler best fits your lifestyle—whether you need quiet, adaptable cooling for off-grid excursions or quick, dependable cooling for lengthy trips.
What Is A Compressor Cooler?
Similar to a home refrigerator, a compressor cooler is a type of refrigeration appliance that actively cools its interior using a compressor and refrigerant system. This technology is one of the best choices for keeping food and drinks cold while traveling or camping since it enables accurate temperature control and quick chilling.
A compressor cooler uses internal coils to circulate a refrigerant as part of its cooling operation. The refrigerant gas is compressed by the compressor, increasing its pressure and temperature. The cooler’s internal temperature is successfully lowered when the gas moves through the condenser and evaporator, absorbing heat from within and expelling it outside. Depending on the model, this technique enables the cooler to operate consistently in spite of outside heat and achieve temperatures low enough to freeze objects.
Compressor coolers can be used at home, in cars, or in RVs because they are usually powered by AC energy, DC electricity from vehicles, or a mix of the two. Convenience and efficiency are increased by the computerized temperature controls, integrated thermostats, and energy-saving modes included in many models.
These coolers are perfect for people who require dependable, quick, and steady cooling, particularly in settings with potentially high temperatures or where exact control is required. Nevertheless, when operating at maximum power, they often use more energy and are louder and heavier than absorption coolers.
All things considered, compressor coolers are ideal for lengthy road trips, RV excursions, and any circumstance requiring quick, dependable cooling. They offer a reliable way to keep drinks cold and perishable goods fresh, even under harsh circumstances, by combining performance with adaptability.
What Is An Absorption Cooler?
An absorption cooler is a type of refrigeration device that cools its interior using a heat-driven chemical process instead of a mechanical compressor. This technology is frequently utilized in RVs, boats, and off-grid configurations where minimal vibration, flexible power sources, and quiet operation are important factors.
In order for absorption coolers to function, a refrigerant solution—typically ammonia, water, and hydrogen must be circulated through a closed system. The evaporation and condensation cycle, which extracts heat from the cooler’s interior, is powered by a heat source, such as propane gas, 12V DC, or home AC electricity. Absorption coolers work almost silently and with little mechanical movement because the cooling process doesn’t require a compressor, which makes them perfect for settings where noise could be an annoyance.
The range of power options available to absorption coolers is one of their primary benefits. Numerous devices have the ability to switch between gas, household electricity, and vehicle electricity, enabling customers to continue cooling in a range of environments. They are particularly well-liked for extended RV travel, isolated cottages, or boat excursions where a dependable power supply might not always be accessible.
Absorption coolers do have certain restrictions, though. They may have trouble maintaining extremely low temperatures, particularly in hot regions, and generally cool more slowly than compressor types. Additionally, they typically need more careful leveling to function properly, especially on uneven surfaces like boats or RVs, and are less energy-efficient when operating on power.
All things considered, absorption coolers are perfect for consumers who value quiet, adaptable cooling with a variety of power sources and who don’t need extremely quick temperature decreases or freezing capabilities. They deliver consistent cooling while reducing noise and mechanical complexity, making them a dependable option for long journeys and off-grid excursions.
Comparison of Cooling Performance

Cooling performance is one of the most important considerations when comparing compressor coolers to absorption coolers. Although both methods are intended to keep food and beverages at acceptable temperatures, they differ greatly in terms of speed, temperature range, and dependability in different scenarios.
Compressor coolers are excellent for cooling quickly and precisely. The cooler can swiftly achieve extremely low temperatures because the compressor actively circulates refrigerant. Many versions are even capable of freezing objects, which makes them ideal for lengthy journeys or circumstances when it’s crucial to maintain a particular temperature. They can sustain steady cooling within the unit even on hot summer days because their performance is essentially unaffected by the surrounding temperature. Because of this, compressor coolers are perfect for users that require quick, dependable, and consistent cooling in any setting.
Absorption coolers, on the other hand, use a heat-driven chemical process that is by nature slower than mechanical compression. Although they can keep food and beverages cold, they typically take longer to achieve the right temperature and could have trouble maintaining extremely low temperatures in hot weather. Without a reliable and sufficient power source, absorption coolers are less able to handle severe heat or freeze objects, but they are excellent at providing continuous, quiet cooling.
Consistency is another distinction. While absorption coolers may need careful leveling, especially on uneven surfaces like RVs or boats, compressor coolers offer consistent temperatures regardless of cooler orientation. Furthermore, absorption coolers frequently have manual or less responsive settings, whereas compressor coolers typically have digital controls and thermostats for accurate changes.
In general, a compressor cooler is the best option if quick cooling, accurate temperature control, and freezing capability are top concerns. Particularly in settings where power sources fluctuate or noise levels need to be kept to a minimum, absorption coolers are more appropriate for quiet, adaptable, and consistent cooling. Users can select the best cooler for their unique travel or storage requirements by being aware of these performance variations.
Power Options and Energy Efficiency
When choosing between a compressor cooler and an absorption cooler, energy efficiency and power options are crucial because they dictate how long and where the cooler may be utilized efficiently.
Electricity is usually needed for compressor coolers, either via a DC car connection, an AC outlet, or both. They actively circulate refrigerant using a mechanical compressor, which can use more energy than absorption coolers, particularly when freezing or maintaining extremely low temperatures.
However, thermostats, digital controls, and energy-saving modes are frequently included in contemporary compressor models, enabling users to maximize power usage without compromising cooling efficiency. Because of this, they are especially well suited for usage in RVs, cars, and homes where electricity is easily accessible.
In contrast, absorption coolers are more adaptable when it comes to power sources. Many versions are perfect for off-grid situations or long excursions where electricity may be scarce because they may run on propane gas, AC electricity, or 12V DC. Absorption coolers typically take longer to reach desired temperatures, which can lead to increased energy demand over lengthy periods of time, even if they operate silently and use less mechanical energy. For customers who require various power options or wish to prevent depleting vehicle batteries, they are quite useful.
Compressor coolers are more effective in rapidly reaching and sustaining low temperatures, particularly in warm situations. Absorption coolers are less efficient in extremely hot conditions or when quick cooling is required, but they provide reduced power requirements for consistent, moderate cooling.
Generally, a compressor cooler is the ideal option if quick, reliable cooling using power is your top goal. An absorption cooler offers energy-efficient cooling across several power sources if you require off-grid functionality, silent operation, and variable power options.
Convenience, portability, and size
Portability, size, and general convenience are important factors when deciding between a compressor cooler and an absorption cooler, particularly for outdoor enthusiasts and tourists.
Because they include a mechanical compressor and refrigeration components, compressor coolers are often heavier and more durable. Although several types have wheels or ergonomic handles for better transportation, they are typically heavier and less practical to move about a lot. However, they are perfect for customers that value temperature performance over ultra-light portability due to their small internal layout and effective cooling. Convenience is further improved with digital controls, thermostats, and energy-saving modes, which provide accurate control of cooling settings.
In contrast, because they don’t use moving mechanical parts, absorption coolers are frequently lighter and quieter. They are especially well-suited for boats, RVs, and other settings where silent operation is crucial because of their structure, which usually permits flexible positioning. Many absorption coolers don’t require continuous electrical access because they can run on a variety of power sources, including propane. They may, however, take longer to achieve the desired temperatures, thus users may need to prepare ahead of time when cooling objects before using them.
Another thing to think about is capacity. Compressor coolers are ideal for long vacations or families since they frequently provide more interior room in relation to weight. Due to insulation and construction restrictions, absorption coolers may have a little less useful space, but they make up for it with different power sources and flexible placement possibilities.
In conclusion, customers who value dependable performance and effective cooling—even if it means a larger unit—are most suited for compressor coolers. Absorption coolers are useful for a variety of travel situations and off-grid settings, making them perfect for people who desire silent operation, less weight, and versatility across numerous power sources.
Price and Long-Term Worth
Cost and long-term value are crucial factors to take into account when comparing compressor coolers versus absorption coolers. Determining which cooler provides the best return over time requires an understanding of the initial expenditure and possible maintenance needs.
Because of its mechanical parts, digital controls, and improved cooling capabilities, compressor coolers typically cost more up front. Size, features, and brand all affect price, but the investment is frequently justified by quicker cooling, accurate temperature control, and the capacity to freeze goods. They require little upkeep over time—usually just cleaning and sporadic power connection inspections making them a reliable choice for long-term RV use or frequent travel.
Basic types of absorption coolers are typically less expensive at first, but more expensive models with several power options can get close to the price of a compressor cooler. Their ability to run on propane, AC, or DC electricity is a benefit. But, especially for off-grid or boat use, they might need extra care to guarantee correct leveling, routine cleaning, and maintenance of gas or electrical components.
For consumers that require precise performance over many years, a compressor cooler offers dependable, consistent cooling in terms of long-term value. An absorption cooler is perfect for some settings, such as RVs, yachts, or off-grid cabins, because it provides value through power flexibility and silent operation.
The optimal investment ultimately relies on how often you use it, how you travel, and how important quick, reliable cooling is compared to silent, multi-source operation. Every kind of cooler offers a unique ratio of price to long-term advantages.
Pros And Cons
You may make an informed choice depending on your travel and cooling requirements by being aware of the benefits and drawbacks of compressor coolers versus absorption coolers.
Compressor coolers
Pros:
- Quick and effective cooling: Capable of freezing objects and rapidly reaching low temperatures.
- Accurate temperature control: Consistent and precise cooling is made possible by digital thermostats.
- Dependable in hot weather: The temperature of the surrounding air usually has little effect on performance.
- Versatile power options: AC, DC, or both are supported by many models.
Cons:
- Bulkier and heavier: Less practical for regular transportation.
- Higher initial cost: Compared to absorption coolers, the initial investment is typically higher.
- Noisy operation: Compared to absorption types, mechanical compressors produce more noise.
- Increased energy use: particularly when cooling to extremely low temperatures.
Absorption Cooler
Pros
- Quiet and vibration-free: Perfect for off-grid configurations, boats, and RVs.
- Flexible power sources: Provide adaptability by operating on propane, AC, or DC.
- Lightweight: More convenient to store and move in cars or small areas.
- Low-maintenance mechanical components: The chance of mechanical failure is decreased when there are fewer moving parts.
Cons:
- Slower cooling: It takes more time to get the right temperature.
- Heat affects performance: In extremely hot regions, performance may suffer.
- Restricted freezing ability: Generally unable to freeze goods.
Verdict:
For quick, dependable cooling and accurate temperature control, go with a compressor cooler. For off-grid mobility, multiple power options, and quiet operation, pick an absorption cooler. This side-by-side comparison helps you choose the cooler type that best suits your lifestyle by highlighting the trade-offs between performance, portability, affordability, and convenience.
Final Verdict
Your unique requirements, travel preferences, and cooling objectives will ultimately determine whether you choose an absorption cooler or a compressor cooler. Both offer powered cooling without the use of ice, but each offers unique benefits that make it more appropriate in particular circumstances.
The quick and effective cooling, accurate temperature control, and freezing capabilities of a compressor cooler make it unique. Users who frequently travel in hot conditions, take lengthy road journeys, or require dependable refrigeration for perishable foods may find it ideal. Its performance and longevity make it a reliable option for prolonged usage in circumstances when maintaining a constant temperature is essential, despite the fact that it is heavier and somewhat noisier.
On the other hand, an absorption cooler performs exceptionally well in terms of being silent, adaptable, and versatile. It is ideal for boating, RV camping, and off-grid excursions because it can run on propane, AC, or DC power. Its silent operation and lighter construction make it useful in small spaces or places where noise and vibration must be kept to a minimum, even if it cools more slowly and struggles under intense heat.
If you require quick, accurate, and reliable cooling for frequent or lengthy travel, choose a compressor cooler. If you value off-grid ease, multi-power flexibility, and silent operation, go with an absorption cooler. You can choose the cooler that best balances performance, convenience, and long-term value by assessing your trip frequency, power availability, and cooling needs. Both kinds work well, but tailoring the technology to your way of living guarantees that your food and drinks remain cool and fresh wherever your travels take you.
